Our brains communicate with electrical and “Women of the West Imagined: Persian Occidentalism, Euro-eroticism, and Modernity.â€chemical signaling, but scientists have discovered that light stimulation could hold potential keys to manipulating neuronal communication pathways that influence motor control, sensory perception, memory, neurochemical production and mood – or cellular virtual reality, as a report from the Journal of Cell Biology describes it.
With the roll out of the White House's $300 million BRAIN Initiative in 2013, interest in uncovering the secrets of the human brain has accelerated and now includes many government agencies, public/private partnerships and universities.
Dating back to at least 1971, optogenetic research has matured enough to gain the attention of organizations such as the NIH, DARPA and IARPA, who are exploring the role that light-sensitive cells could soon play in fields surrounding neurobiological, including physical and mental health, human-machine interfacing, and advancing artificial intelligence through reverse brain engineering.
Current optogenetic experiments rely on extracting "opsins" (light-sensitive proteins) from plants which can be introduced to mammals by methods including injection and infection via adenovirus.
Once delivered into an organism, opsins can be expressed in eye, brain or skin cells, allowing their light-sensitivity to be remotely activated or silenced with timed pulses of light in different color wavelengths across the light spectrum that can target multiple bodily systems and cause a variety of biological effects.
Researchers have suggested however that introducing opsins into an organism may not be a long-term requirement as methods are sought for using optogenetics on mammalian cells that respond naturally to light, such as those in the human retina.
As part of the BRAIN Initiative, scientists have been working on neuronal barcoding and completing a detailed online brain atlas for researchers. This is hoped to eventually provide a detailed circuit diagram of every neuron and synapse in the brain, which would allow various neuronal patterns to be identified so they can be triggered for the desired effect.
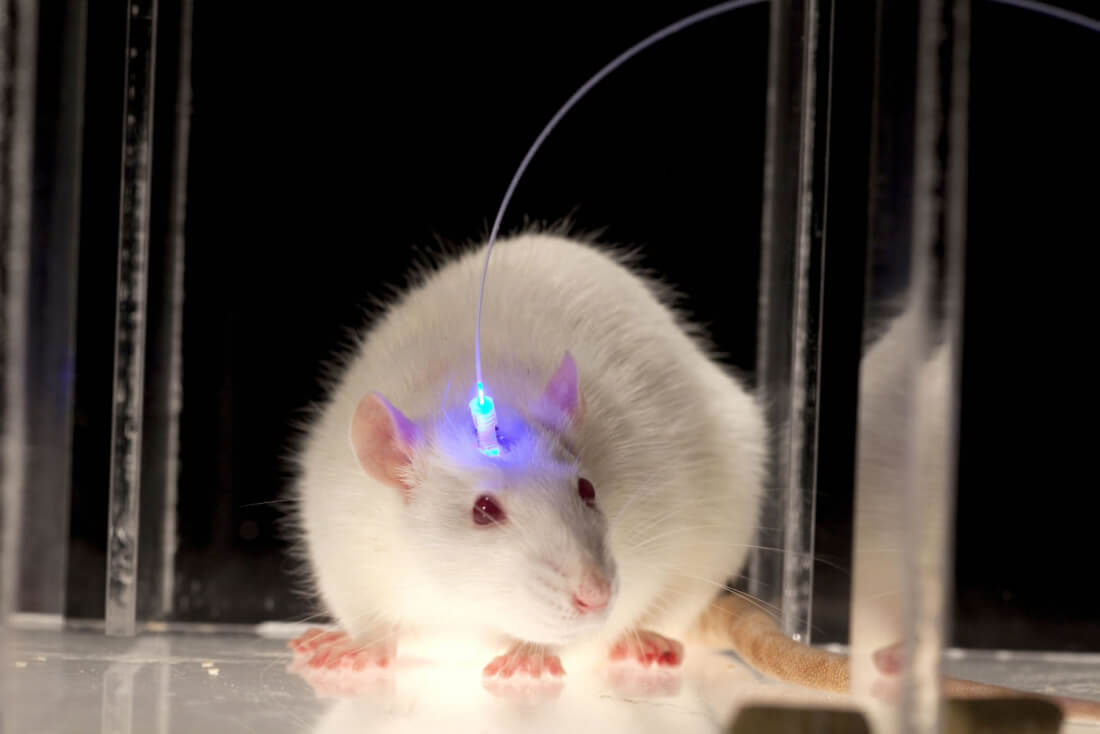
If targeted precisely enough with the appropriate light, it's thought that optogenetics could be used by manipulating neural circuits involved with pain, fear, reward, wakefulness and social behaviors. In one Yale study, for example, mice were infected with a virus which made their neurons sensitive to blue light. Scientists then used that light pathway to activate predatory behavior.
"...The researchers used a tiny optic fibre to shine a blue laser on the amygdala. This prompted the animals to tense their jaw and neck muscles... 'It's not just physiological, it's hunting, biting, releasing and eating. Those are motor sequences that require a lot of information...' [said an MIT neuroscientist]"
In 2015, optogenetics was combined with CRISPR to develop a set of photoactivatable tools that enable the editing of an organism's genome through the external use of light. Said tools can control the location, timing and reversibility of the genome editing process, whether that be activating, repressing or modifying a gene.
Optogenetics is also mentioned as an integral feature of the DARPA-funded Neural Engineering System Design (NESD) program, a joint effort between six teams who are aiming to create an implantable neural interface over the next four years that is capable of high resolution brain-to-machine communication. Such advancements, for instance, could facilitate the development of mind-controlled prosthetics featuring touch sensation like the DARPA-backed 'Luke' arm (previously known as the 'Deka' arm).
In the past, DARPA has looked to optogenetic memory manipulation techniques for treating veterans with traumatic brain injury and/or PTSD through memory restoration or deletion.
More recently, during a November 2017 mental health conference with 30,000 attendees in Washington D.C., optogenetics was noted for the impact it's having on the ability to study the brain. According NPR science correspondent Jon Hamilton, the technology has allowed aspects of human mental health disorders to be reproduced in animals, aiding the mapping of neuronal circuits involved with issues such as depression.
Companies interested in the application of optogenetic technologies have begun emerging over the last decade, particularly since the FDA approved the technology in 2015 for use in treating an eye disorder known as "retinitis pigmentosa."
The approval prompted a clinical trial and optogenetic developments have since been used to restore partial vision in patients who were described as being "profoundly blind." Chronic pain management, epilepsy and Parkinson's are among many health issues that researchers are experimenting with addressing through optogenetics.
The technology is also contributing to other areas of research such as "sonogenetics," which uses low-pressure ultrasound to activate ultrasonically sensitized neurons. This is another area of interest for DARPA, which has funded Columbia University's endeavor to stimulate neurons using ultrasound and believes it could eventually lead to a magnetic version of the technology called "magnetogenetics."
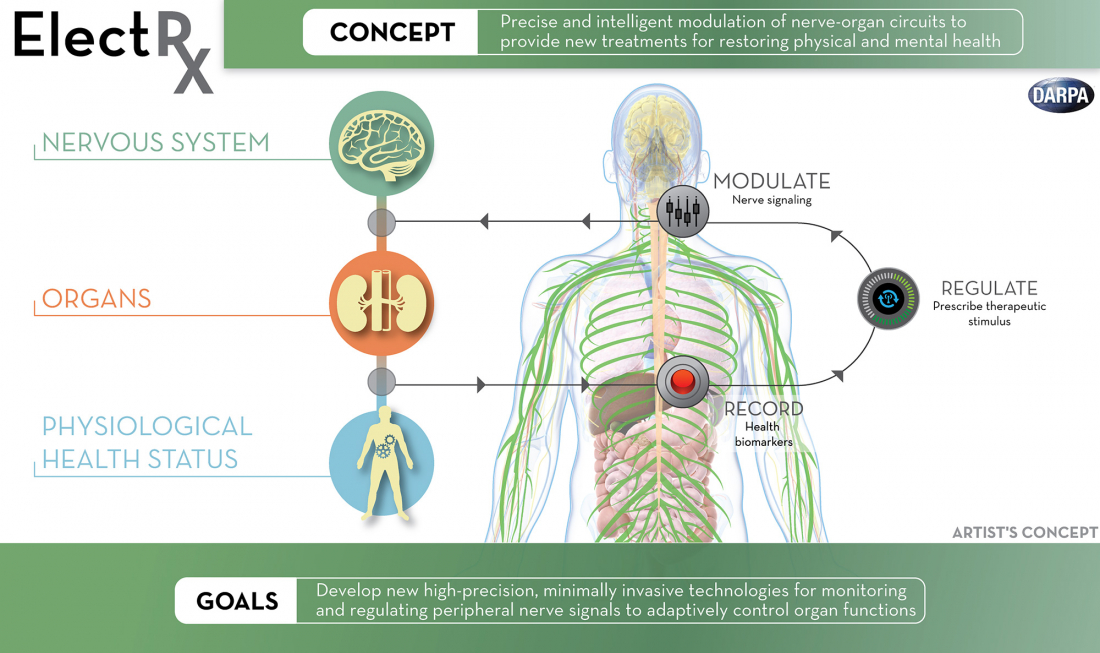
To investigate the therapeutic use of optogenetics, acoustics and electromagnetic fields, DARPA launched the ElectRX (Electrical Prescription) program in 2015, which is capable of stimulating, modulating and monitoring the body's peripheral nervous system. The research agency is also exploring how artificial intelligence could be used in closed-loop brain implants, such as the ability to detect patterns associated with mood disorders.
With enough progress, it's believed that optogenetics and its surrounding bodies of research may open the door to real-time brain mapping and biofeedback technologies, which could be used to treat all manner of ailments on the fly through closed-loop neuromodulation signals coming to and from an implanted device, ultimately eliminating the need for pharmaceuticals.
 Super Bowl LIX livestream: Watch Eagles vs Chiefs on Tubi
Super Bowl LIX livestream: Watch Eagles vs Chiefs on Tubi
 Best iPad deal: Save over $100 on the Apple iPad 9th Gen
Best iPad deal: Save over $100 on the Apple iPad 9th Gen
 Best coffee maker deal: Save $20 on the Ninja Single
Best coffee maker deal: Save $20 on the Ninja Single
 Hurricane Milton: Spaghetti models track the storm’s Florida path
Hurricane Milton: Spaghetti models track the storm’s Florida path
 Will Oracle take over TikTok? Trump says he'll make a decision in 30 days
Will Oracle take over TikTok? Trump says he'll make a decision in 30 days
 The best early October Prime Day drone deals
The best early October Prime Day drone deals
 How to watch Miami vs. Cal football livestreams: kickoff time, streaming deals, and more
How to watch Miami vs. Cal football livestreams: kickoff time, streaming deals, and more
 Early Prime Day deals on noise
Early Prime Day deals on noise
 Best Presidents' Day deal: Save $250 on Peloton Bike
Best Presidents' Day deal: Save $250 on Peloton Bike
 How to factory reset a PS4
How to factory reset a PS4
 Google's data center raises the stakes in this state's 'water wars'
Google's data center raises the stakes in this state's 'water wars'
 MotoGP livestream: Watch the 2024 Japanese Grand Prix for free
MotoGP livestream: Watch the 2024 Japanese Grand Prix for free
 Nearly a quarter of iPhone users say green bubbles are a dating dealbreaker, new survey reveals
Nearly a quarter of iPhone users say green bubbles are a dating dealbreaker, new survey reveals
 Nearly a quarter of iPhone users say green bubbles are a dating dealbreaker, new survey reveals
Nearly a quarter of iPhone users say green bubbles are a dating dealbreaker, new survey reveals
 October Prime Day unlocked phone deals: Samsung Galaxy S24 FE, Motorola razr, and more
October Prime Day unlocked phone deals: Samsung Galaxy S24 FE, Motorola razr, and more
 Best Bluetooth speaker deals: Prime Big Deal Days 2024
Best Bluetooth speaker deals: Prime Big Deal Days 2024
 NASA releases photo of ocean world. It shows why NASA's going there.
NASA releases photo of ocean world. It shows why NASA's going there.
 Kamala Harris appears on 'Call Her Daddy' podcast for 40
Kamala Harris appears on 'Call Her Daddy' podcast for 40
Display Tech Comparison: IPS vs. VA vs. TN vs. QDHow to increase retention on TikTok and YouTube videosBest MacBook deal: 2025 M4 MacBook Air for $829Alcaraz vs. Munar 2025 livestream: Watch Queens Tennis for freeVidCon 2025 Tips: Writing a video script for YouTube, TikTok, and moreBest robot vacuum deal: Save $350 on the Eufy X10 Pro OmniHow to increase retention on TikTok and YouTube videosNvidia's RTX 5080 is Actually an RTX 5070Apple has a new version of iPhone's default ringtoneBest charger deal: Save $18 on Anker 3Inter Miami vs. Porto 2025 livestream: Watch Club World Cup for freeBest water flosser deal: Save $12 on Waterpik CordlessBest TV deal: Save $199.90 on 100Glastonbury 2025 livestream: How to watch Glastonbury for freeBest vacuum deal: Get the Dyson V8 Plus cordless vacuum for $120 offNYT Strands hints, answers for June 20Best Apple deal: Save $100 on the Apple Studio DisplayBest Apple deal: Save $100 on the Apple Studio DisplayNvidia's RTX 5080 is Actually an RTX 5070Best robot vacuum deal: Save $350 on the Eufy X10 Pro Omni 'Jane the Virgin' respects consent in the kind of scenes we need on TV This portable 'Super Smash Bros. Melee' system is a dream come true Google reveals I/O 2018 developer conference dates: May 8 Disney unveils 'A Wrinkle In Time' Barbies and we're crying tears of joy Andrew Lincoln will narrate Harry Potter audiobook about Quidditch Cape Town will run out of water on April 12, due to historic drought New Google Chrome update mutes all irritating audio on websites Reese Witherspoon has 3 legs: A 'Vanity Fair' Photoshop story 'Murphy Brown' returns to save us from the fake news of the Trump era Cryptocurrency exchange loses $400 million worth of coins in massive NEM hack HomePod only works with Apple Music, and that's a big mistake Maisie Williams announces 'Game of Thrones' return date Meryl Streep heads back to TV for 'Big Little Lies' Season 2 CyreneQ on why she still loves Snapchat, builds AR as others leave That weird 'Crocodile Dundee' sequel trailer may just be a marketing stunt CNN throws in the towel on Casey Neistat and Beme Ford X incubator will research new transit ideas Download this: Sweatcoin app bribes you to exercise with real prizes Snapchat update lets you share camera roll pics without white borders Man orders Bitcoin miner on Amazon, gets sent 'The Boss Baby' on DVD
2.4221s , 10219.2265625 kb
Copyright © 2025 Powered by 【“Women of the West Imagined: Persian Occidentalism, Euro-eroticism, and Modernity.â€】,Fresh Information Network